- You are here
- Home
- Guide to Africa
-
- Mozambique Guide
- Mozambique National Parks and Game Reserves
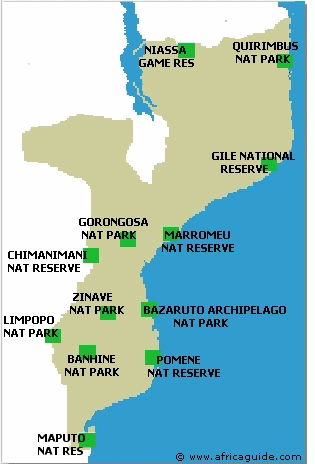
Mozambique National Parks and Game Reserves
Parent page
On this page
Introduction
One of the main tourist attractions of Mozambique are the environmental conservation areas.
Presently, they cover about 12.6% of the total country's surface, and comprise 6 National Parks and 6 National Reserves.
The National Parks and Reserves are circumscribed public spaces, delimited, which represent the natural national heritage. They aim to protect the biodiversity and fragile ecosystems as well as animals' species and vegetation.
Besides presenting the effort that has been made in order to continually protect the Mozambican biodiversity, this brochure also shows the beauties with exceptional characteristics on, both leisure and environmental education in large scale, promoting, at the same time, the ecological tourism.
Mozambique is not just a travel destination, it is a once in a life time experience. A countless breathtaking variety of landscape is offered to the visitor, in terms of flora, as well as fauna.
Location: The Niassa Game Reserve (NGR) is situated in Niassa Province.
Area: 42,000 km2
Access: Access by road via Marupa district (there is a road linking Marrupa with Lichinga which is being tarred on a radius of about 150km). By plane to Lichinga and then by road from Lichinga to Marrupa, Marrupa to the Game Reserve. The NGR has also an airstrip (Mecula) which can be used for landing and takeoff of aircrafts. The Pemba airport also serves as an entry point into the NGR. It can also be used, the road from Montepuez district in Cabo Delgado Province.
Best viewing season: During winter season, in the weak months, between April and October.
Attractions: Landscape diversity such as miombo forests, mountain forests, riverine vegetation, open savannah and prairies. Fauna: Lions, leopards, wild dog (wolves) (major population of the country), elephants, buffaloes, gondongs, zebras, elands, pala-palas, ox-horse, kudos, inhacoses (waterbucks), impalas, cinereous kid, kid of rocks.
Viewing hours: The NGR can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: It is one of the world's major natural reserves and the biggest, in Mozambique. The NGR is presently the conservation area with the widest range, of wild fauna species in the country, especially the population of elephants estimated at 13,000 pachyderms. A new species of lizards was discovered recently in the NGR.
Location: The Quirimbas National Park (QNP) is situated in Cabo Delgado Province, covers six provincial central districts and comprises 11 islands in the Archipelago of Quirimbas.
Area: 7,506 km2
Access: The QNP can be accessed by air travel, from all provincial capital cities (via Lam and Air Corridor) and regional flights from the RSA, Tanzania, Kenya to Pemba and later on by road leading to the inner park or by small aircrafts available at Pemba airport or through local tourist agents or by sea to the park islands
Best viewing season: In the weak months, between April and October.
Attractions: Islands, sea environment with coral-reefs and more than 375 fish species. Wild Life (great mammals, birds, and other species). Culture (Ibo Island), Banco de Sao Lazaro with unique features. Mangroves, mountains, miombo and savannah forests.
Fauna: Marine species: whales, dolphins, dugongs, turtles, sharks and wide range of exotic fish species, and a diversity of interest for sports, fishing charters and diving. Land Species: elephants, buffaloes, pala-palas, elands, mabecos (dog-hunters), lions, leopards, spotted hyenas, jackals, crocodiles. A wide range ol bird species.
Viewing Hours: The QNP can be visited daily from 7.30 to 16.30
Particularities: This Park has a great potential tor performance ol various ecotourism activities apart from having the particularity ol combining within its limits different tourist attractions, such as the sun and the sea, wild and cultural life. Its coral-reels are ideal for diving and snorkelling.
Location: The Gile National Reserve (GNR) is situated in Zambeze Province, covering the districts of Gile and Pebane. The GNR was initially declared at first proclaimed Partial Game Reserve of Gile in 1932.
Area: 2,860 km2
Access: Road access from Zambezia capital city, Quelimane or from other points of the Province. Guests are urged to travel in 4x4 vehicles due to the conditions of the roads. Other access is also possible from Nampula city (Nampula Province).
Best viewing Season.- In the weak months during winter, between April and October. However, the best period for bird watching is during the rain season (November-March).
Accommodation: There is no tourism development in the GNR. Accommodation under the form of camping can be arranged through the GNR administration in the Musseia main campsite and in the Lice inspection campsite.
Attractions: It is mainly made up of miombo forest, dambos, reforested savannah and riverine vegetation along various rivers and rivulets. Of great interest the granitic Kopjes' habitats which are either inside or around the GNR.
Fauna: There are listed 95 mammal species, amongst which the elephants, lions, leopards, wild dogs (wolves), spotted hyenas (crocutacrocuta), pala-palas, kudos, impalas. There are also listed 114 bird species.
Viewing Hours: The GNR can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The mounts surrounding the Reserve are ideal for mountaineering. The GNR can have tourist connections, with the beautiful Pebane beach, the Gurue landscape, the Moebasse beach and with the first and second islands, (Zambeze Province) as well as with Mozambique Island (Nampula Province).
Location: The Gorongosa National Park (GNP) is situated in Sofala Province; it lies on the south edge of the Great Rift Valley, 80km north-west of Beira.
Area: 5,732 km2
Access: By road either from Chimoio or Beira city.
Best viewing season: During winter season, in the weak months, between April and October.
Accommodation: Camping.
Attractions: Gorongosa Mountain Ridge, Cheringoma Plateau, Urema Lake. The house of lions is also one of the park's attractions, as well as the rivers and lakes, river Murombo's waterfall and the Gorongosa mountain ridge cascades.
Fauna: Buffaloes, elephants, ox-horses, hippos, zebras, inhacoses (waterbucks), elands, oribis, impalas, pala-palas, changes, pivas, facoceros (phacochoerus aethiopicus), imbabalas (females bushbucks), lions, leopards, spotted hyenas (crocuta crocuta), wild dogs (wolves) and crocodiles.
Viewing hours: The GNP can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: It is one of the world's most known conservation areas of Mozambique. With tremendous potential for bird watching and touring around Gorongosa Mountain Ridge as well as guided visits to watch the animals.
Location: The Marromeu National Reserve (Marromeu NR) is situated in Sofala Province.
Area: 1,560km2
Access: By road, from Beira city. Best viewing season: During winter season, in the weak months, between April and October.
Accommodation: There is no tourist development in Marromeu RN. Accommodation under the form of campsite can be arranged through the administration of the Reserve.
Attractions: It has great population of buffalos and other mammals, but the most important attraction is the great quantum of birds, both seasonal and permanent.
Fauna: Lions, leopards, buffaloes, elephants, kudos, impalas, changes, inhalas, wild boars, ox-horse, elands, wild pigs.
Viewing hours: The Marromeu NR can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The Marromeu NR protects the major humid area along the delta of Zambeze. Due to the great importance of the conservation of the habitat, the Marromeu NR was declared as "RAMSAR Area"
Location: The Chimanimani National Reserve (CNR) is situated in the Sussundenga district, Manica Province.
Area: 640 km2
Access to CNR is possible by road, either from Chimoio city or via a road, from the airports of the cities of Tete, Chimoio and Beira. It is advisable to travel in a 4x4 due to the state of the roads.
Best viewing season: Throughout the year. During the winter months (June to August) the temperature scale, can fall below zero degrees Celsius.
Accommodation: Basic campsites are available in Chikukwa and Mahate.
Attractions: The CNR has an intact ecosystem and rich in biodiversity especially in the mountainous areas, landscapes, archaeological tools, (rupstart paintings), intact beliefs and traditional structures. It has a great diversity of species of plants and endemic species of birds, reptiles and butterflies.
Fauna: Buffaloes, oribias, elands, blue goats, cinereous kids, kids of rocks, imbabalas (female bushbucks), changanes, pala-palas, changes, pivas and facoceros(phacochoerus aethiopicus). A wide variety of bird species and reptiles, including endemic species.
Viewing Hours: The RNC can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The RNC protects a series of ecosystems of great value, including prairies and high mountain vegetation. It has favourable conditions for the practice of various activities: Mountaineering, safaris, canoeing, equitation and cultural tourism. The LNP is part of the Chimanimani Transfrontier Conservation area.
Location: The Bazaruto Archipelago National Park (BANP) is situated in the districts of Vilanculos and Inhassoro in Inhambane Province. Comprises 5 islands in the Bazaruto Archipelago, 20 km from the coast of Vilanculos and Inhassoro.
Area: 1,400 km2
Access: Either by road or plane to Vilanculos or Inhasooro and later on by air or sea into the islands.
Best viewing season: Throughout the year.
Attractions: It has a wide range of marine species diversity and it is considered one of the worlds major dive centers. Beaches with transparent and clear waters and an avifauna rich in species.
Fauna: Dugongs, various species of whales, dolphins, sea turtles, sharks and rays. Various species of exotic birds, including the flamingo.
Viewing hours: The Bazaruto Archipelago National Park, can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The BANP has sea and road component. It was set up to protect sea fauna species namely the dugongs, marine turtles and dolphins and also the weak ecosystems of the islands. It is worth stressing that about 150 dugongs occurring in this area, are a major population in the coast of East Africa.
Location: The Zinave National Park (ZNP) is situated along River Save in Inhambane Province.
Area: 4,000 km2 Access:
Access by road from Inhambane city and Gaza or other points of the province, being advisable to travel in 4x4 vehicles due to the conditions of the road (precarious roads).
Best viewing season: In the weak months during the winter season, between April and October.
Accommodation: There is no tourist development in the ZNP. Accommodation under the form of camping can be arranged through the local administration in the main campsite.
Attractions: The ZNP has a diversity of landscapes namely: miombo forests, bushes, riverine vegetation. The ZNP has also lagoons.
Fauna: Kudos, inhalas, imbalabalas (female bushbucks), hippos, impalas, inhalas, changes, chipenes, cinereous kid kid of rocks, changanes, leopards, lions, cheetah, spotted hyenas (crocuta crocuta).
Viewing hours: The ZNP can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: It is part of the Great Limpopo Transboundary Conservation Area Programme.
Location: The Limpopo National Park (LNP) is situated west of Gaza Province, near the South Africa border and south of Zimbabwe border (it comprises an area ol 200 km).
Area: 10,000 km2
Access: The LNP can be accessed via beaten road through Ginyondo Border Post leaving from Kruger Park and the Paluri Border Post (natural road). From inland Mozambique it is possible to access the park by road leaving from Massingir and Mapai.
Best viewing season: In the weak months, Irom April to October.
Accommodation: The LNP has two campsites with accommodation facilities - tourists are urged to bring along their own tents and supplies). Additionally, there are campsites available along the Safari routes (Paluri-Massingir) Tambolie, Mamba Pan and Machamba.
Attractions: This park has the particularity of presenting a landscape which is still intact almost across its surface with 10 distinct landscapes. In an indoor environment visitors can gaze at almost 100% of Southern African species of wild fauna, including the Big Five. The Massingir Dam, the zone ol river Shingwedzi and Mapai are attracting zones in terms of fauna, and culture.
Fauna: Big Five, elephants, white rhinos, buffaloes, lions, leopards. Other Animals: wild dogs, hippos, zebras, impalas, kudos, wild boars, wild pigs, cinereous kid, kid ol rocks, ox-horses, inhalas, spotted hyenas, pala-palas, pivas, changes, oribis (ourebia ourebi) and crocodiles.
Viewing Hours: The LNP may be visited daily Irom 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The LNP is part ol the Great Limpopo Transboundary Conservation Programme. The area ol river Shingwedzi is ideal for dismounted tourism based on wild fauna. The Massingir Dam is favorable for diverse adventure water sports. Cultural tourism may also be conducted in Mapai.
Location: The Banhine National Park (BMP) is situated in Gaza Province.
Area: 6,000 km2
Access: By road from Inhambane village or Gaza Province (roads in precarious conditions).
Best viewing season: In the weak months during the winter season, between April and October.
Accommodation: There is no tourist development in the BNP. Accommodation under the form of camping can be arranged through the BNP administration in the main campsite.
Attractions: The park has well distinct landscapes like in human areas, open savannah, mopane and miombo forests.
Fauna: Lions, leopards, kudos, impalas, changes, inhalas, cinereous kid, hippos, oribis, (ourebia ourebi), pala-palas, ostriches and crocodiles.
Viewing Hours: The BNP can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: It forms part of the Great Limpopo Transfrontier Conservation Area Programme. It has the most humid area inland Mozambique, ecologically regulated by trends related to cyclical rainfall fluctuations and draughts.
Location: The Pomene National Reserve (PNR) is situated in Massinga District in Inhambane Province
Area: I26km2
Access: Access by road either from Maputo or Beira city. Guests are urged to travel in a 4x4 vehicle. Access is also possible by plane from Inhambane airstrip.
Best viewing season: throughout Ihe year.
Attractions: The different landscapes of the Reserve such as vegetation of the dunes, savannahs, mangroves and marshes are a combination which offers great ecotourism opportunities for the PNR.
Fauna: Ox-horses, wild boars, cinereous kid, chipenhes, irnpalas, monkey-dogs and grey monkeys. A wide range of bird species.
Viewing hours: the PNR can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: Set of land and sea habitats, vegetation of dunes and sandy soil forests.
Location: The Maputo National Reserve (Maputo NR) is situated in Maputo Province, inside Matutuine district.
Area: 778 km2
Access: From the country's capital Maputo crossing the Bay and then by road from Catembe or simply by road from Boane.
Best viewing season: Throughout the year.
Accommodation: Milibangalala camping area. A couple of community lodges in areas near the Maputo NR. Various tourist undertakings are available in the south of the Maputo NR, in the area of Ponta do Ouro.
Attractions: Various beaches along the coast (Ponta Chemucane, Ponta Menbene, Ponta Milibangalala and Ponta Dobela): Different landscapes (sandy soil forests, humid land forests, marshes, mangroves, dunes). Lagoons (Piti, Maunde, Nela, Machai, Chinguti). Holy and cultural places (ideal for cultural tourism).
Fauna: Elephants, changes, kudos, pivas, changanes, cinereous kid, kid of rocks, crocodiles. A wide variety of bird species. The marine fauna is very varied, including whales, dolphins, marine turtles, which build nests along the coast and countless fish species.
Viewing Hours: The Maputo NR can be visited daily from 7h30 to 16h30.
Particularities: The Maputo NR protects one of the most valuable habitats (Maputoland regional centre of endemism). The MNR has a scenic beauty with a diversity of habitats, landscapes and sea sceneries of exceptional beauty. The reserve is an ideal place for watching animals and birds, and offers opportunities for sports fishing, diving, canoeing, with a great peculiarity of being a strategically situated destination, because it receives national tourists from South Africa and Swaziland. It forms part of the Lubombo Transfrontier Conservation Area Programme.